Difference between revisions of "Git 101"
(→GitLab) |
|||
| (15 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
=== Putting a new project/folder under version control === | === Putting a new project/folder under version control === | ||
This section uses the example of an EPICS IOCs. For a different type of project, just skip the reference to `xxx` (first 2 lines in the repo initialization). | ==== GitHub vs GitLab: What should I use? ==== | ||
===== GitHub ===== | |||
GitHub is typically used for public project, to be shared accros user facilities (e.g. apstools, MDA_Utilities...) | |||
* GitHub organizes repositories using this pattern: https://github.com/ORGANIZATION/REPOSITORY, where "ORGANIZATION" is either a single user account (i.e. your own GitHub account) or a named organization (e.g. BCDA-APS or APS-29IDC-MM). | |||
* It is recommended to use an organization vs individual account to host shared project (e.g. beamline software). | |||
* The naming convention recommended for a given beamline organization is: APS-SSS-GGG | |||
** SSS: sector, beamline, and station, if relevant (e.g. 29IDC) | |||
** GGG: operating group (e.g. MM for XSD - Magnetic Material) | |||
* BCDA organization: https://github.com/BCDA-APS | |||
===== GitLab ===== | |||
GitLab is typically used for internal project (e.g. IOCs, UI screens...). APS hosts its own GitLab service: https://git.aps.anl.gov. Contact your IT contact to get access. | |||
* GitLab organizes repositories using this pattern: https://git.aps.anl.gov/GROUP/REPOSITORY | |||
* BCDA maintains group for each beamline; ask your BCDA contact to be added to your beamline group. | |||
* It is recommended to use your beamline group vs individual account to host shared project (individual accounts are deleted when employee leave the lab). | |||
==== Example on GitLab ==== | |||
This section uses the example of an EPICS IOCs, i.e. GitLab (steps are the same on GitHub). For a different type of project, just skip the reference to `xxx` (first 2 lines in the repo initialization). | |||
Initialize the local repository: | Initialize the local repository: | ||
Latest revision as of 18:16, 8 August 2024
Practical Step-by-Step Examples
Basic Commit Workflow
This (pull-)edit-add-commit(-push) recipe is all you need for 95% of projects:
- To sync your local repository with the remote repository:
$ git checkout main # Switch to (or confirm you are on) the main branch $ git status # Check the status of your local repo $ git pull # Pull the latest changes from the remote
- To commit a new file:
$ git add <newfile> $ git commit -m 'Added <newfile>"
- To commit changes to an existing file:
$ git add <modifiedfile> $ git commit -m 'Updated <modifiedfile>"
- To commit all changes at once:
$ git commit -am 'Description of changes'
- To push your changes to the remote repository:
$ git push
Note: This workflow assumes you are working with the main branch, and that origin/main has been set as the Upstream Branch.
Putting a new project/folder under version control
GitHub vs GitLab: What should I use?
GitHub
GitHub is typically used for public project, to be shared accros user facilities (e.g. apstools, MDA_Utilities...)
- GitHub organizes repositories using this pattern: https://github.com/ORGANIZATION/REPOSITORY, where "ORGANIZATION" is either a single user account (i.e. your own GitHub account) or a named organization (e.g. BCDA-APS or APS-29IDC-MM).
- It is recommended to use an organization vs individual account to host shared project (e.g. beamline software).
- The naming convention recommended for a given beamline organization is: APS-SSS-GGG
- SSS: sector, beamline, and station, if relevant (e.g. 29IDC)
- GGG: operating group (e.g. MM for XSD - Magnetic Material)
- BCDA organization: https://github.com/BCDA-APS
GitLab
GitLab is typically used for internal project (e.g. IOCs, UI screens...). APS hosts its own GitLab service: https://git.aps.anl.gov. Contact your IT contact to get access.
- GitLab organizes repositories using this pattern: https://git.aps.anl.gov/GROUP/REPOSITORY
- BCDA maintains group for each beamline; ask your BCDA contact to be added to your beamline group.
- It is recommended to use your beamline group vs individual account to host shared project (individual accounts are deleted when employee leave the lab).
Example on GitLab
This section uses the example of an EPICS IOCs, i.e. GitLab (steps are the same on GitHub). For a different type of project, just skip the reference to `xxx` (first 2 lines in the repo initialization).
Initialize the local repository:
$ cp /APSshare/epics/synApps_6_2_1/support/xxx-R6-2-1/.gitattributes . # copy from .gitattributes xxx $ cp /APSshare/epics/synApps_6_2_1/support/xxx-R6-2-1/.gitignore . # copy from .gitignore xxx $ git init # initialize repo $ git add . # stage all relevant stuff $ git status # confirm status $ git commit -m 'first commit yeah!' # commit all staged files
On GitLab, in the corresponding beamline group:
- New project (blue button, upper right corner)
- Create blank project
- Project name: myioc (same spelling as IOC prefix)
- Project slug: myioc (needs to be the same as project name)
- Visibility Level: Internal
- Project Configuration: very important Uncheck initialize repository (to avoid conflict between local and remote)
- Create project
- Code drop-down (blue button, right hand-side): copy the SSH remote URL
git@git.aps.anl.gov:29id/myioc.git
Note: see Why clone with SSH URL.
Back to the local repository, add the reference to the new remote repository:
$ git remote add origin git@git.aps.anl.gov:29id/myioc.git # adds a new remote repository named origin with the given URL) $ git remote -v # lists remote connections to confirm the addition $ git push -u origin main # pushes main to the origin remote and sets it as the upstream
Branching for IOCs Upgrade
This is an example for upgrading from 6.1 to 6.2:
- Make sure your local repository in
synApps_6_1is up-to-date:
$ git checkout main # Make sure your are on the main branch $ git fetch # Fetch the latest changes from the remote $ git pull # Pull (= fetch + merge) the latest changes from the remote
- Create and switch to a new branch named
synApps_6_1(for archive purposes)
$ git checkout -b synApps_6_1 # Create a new branch based on main and switch to it $ git push -u origin synApps_6_1 # Push the new branch to the remote and set origin/synApps_6_1 as the upstream for this branch
- Clone the IOC repository into the
synApps_6_2directory:
$ cd ../../../synApps_6_2/ioc/ # Navigate to the synApps_6_2/ioc directory $ git clone git@git.aps.anl.gov:29id/myioc.git # Clone the repository
You are now ready to upgrade the synApps_6_2/ioc directory from synApps_6_1 to synApps_6_2.
Note: the new main branch now points to the synApps_6_2 directory:
- In the directory
synApps_6_1/ioc/myioc, you will be working on thesynApps_6_1branch (associated to the remote branchorigin/synApps_6_1). - In the directory
synApps_6_2/ioc/myioc, you will be working on themainbranch (associated to the remote branchorigin/main).
Basic Commands
Viewing Changes and Status
- To switch to the
mainbranch:
$ git checkout main
- To see the status of the working directory and staging area (also confirm the current branch you are on):
$ git status
- To list the commit history:
$ git log
- To view differences since the last commit:
$ git diff <file>
- To see tracked files:
$ git ls-files
Committing Changes
- To commit a single tracked file (add file to staging area and commit changes, in two steps):
$ git add <file> $ git commit -m 'commit message'
- To commit all tracked files at once, use option
-a(add to staging area and commit, in a single step):
$ git commit -am 'commit message'
Ignoring Files
.gitignore lists files and folders to be ignored. To update the list, just use any file editor.
Syncing with Remote Repository
- To download updates from the remote repository without merging them:
$ git fetch
- To fetch changes from the remote repository and merge them into your current branch:
$ git pull
- To push local commits to the remote repository:
$ git push
- To list the remote repositories and their URLs:
$ git remote -v
Git Fetch vs. Git Pull
git fetch: downloads changes from a remote repository, but doesn't integrate any of these changes into your working files. It's essentially a safe way to review changes before integrating (merging) them into your local repository.git pull=git fetch+git merge: not only downloads changes from the remote repository but also immediately attempts to merge them into the branch you are currently working on.
Upstream Branch
- The instructions provided here assume that
origin/main(the main branch of the remote repository) is already set as the upstream for your branch. - If an upstream branch has not been set, you will encounter errors when attempting to
pull,fetchorpush:
fatal: The current branch has no upstream branch.
To push the current branch and set the remote as upstream, use
git push --set-upstream origin <branch_name>
- This message is Git's way of telling you that it does not know where to
pull/fetch/pushthe changes from / to. - To resolve this, you can either set the upstream branch as suggested in the error message, or specify the remote name and branch (typically
originandmain, respectively) every time youpull/fetch/push.- To specify the remote & branch name:
$ git fetch/pull/push origin <branch_name> - Or to set the upstream, you would use:
$ git push -u origin <branch_name>
- To specify the remote & branch name:
- The
-uflag stands for--set-upstream:- This flag is used to set a relationship between your local branch and a remote branch:
origin/mainis now the upstream for your current local branch. - Once the upstream is set, you can use
pull,fetchorpushwithout specifying the remote name and branch. Git will automatically know that you're referring toorigin/main.
- This flag is used to set a relationship between your local branch and a remote branch:
Choosing a URL for your remote repository
Why clone with SSH URL
Github support for password authentication (HTTPS) was removed on August 13, 2021. SSH URLs provide access to a Git repository via SSH, a secure protocol. To use these URLs, you must generate an SSH keypair on your computer and add the public key to your account on GitHub.com
If you cloned your repository using the HTTP URL, you can switch to SSH at any time:
git remote -v # check the current repo url origin https://github.com/BCDA-APS/myrepo (fetch) origin https://github.com/BCDA-APS/myrepo (push) git remote set-url origin git@github.com:BCDA-APS/myrepo.git git remote -v # verify the changes to the new url origin git@github.com:BCDA-APS/myrepo.git (fetch) origin git@github.com:BCDA-APS/myrepo.git (push)
More details about HHTPS vs SSH
- HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure):
- Ease of Use: Generally easier for beginners to set up and use, as it often works out of the box without any additional configuration.
- Authentication: Uses username and password for authentication. This can be less convenient because you might need to enter your credentials frequently unless you use a credential helper.
- Security: Secure, as it encrypts the data transferred over the network.
- SSH (Secure Shell):
- Ease of Use: Requires a bit more setup initially. You need to generate an SSH key pair and add the public key to your GitHub account.
- Authentication: Uses key-based authentication. This is more secure and convenient once set up, as you don’t have to enter your username and password regularly.
- Security: Highly secure, with strong encryption of data. The key-based authentication is generally considered more robust than password-based authentication.
Custom aliases
$ git config --global alias.st 'status' # create an alias git st = git status
$ git config --global --list # see list of aliases
$ git config --global --replace-all alias.lg # may need replace-all flag
# to overwrite existing aliases
#### Common aliases:
$ alias.br 'branch'
$ alias.ci 'commit'
$ alias.co 'checkout'
$ alias.st 'status'
$ alias.df 'diff'
$ alias.ft 'fetch'
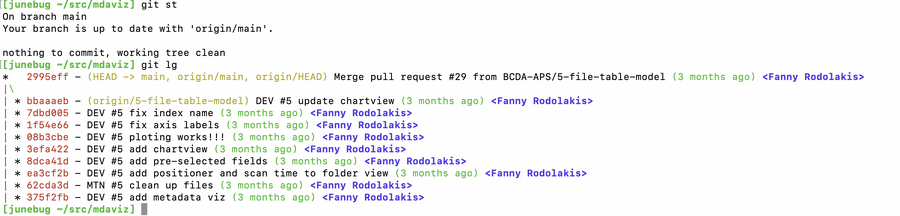
$ alias.lg "log -10 --color --graph --pretty=format:'%Cred%h%Creset -%C(yellow)%d%Creset %s %Cgreen(%cr) %C(bold blue)<%an>%Creset' --abbrev-commit"
This last command sets a global alias lg for git, which transforms the output of git log into a visually structured and color-coded format, displaying the last 10 commits:
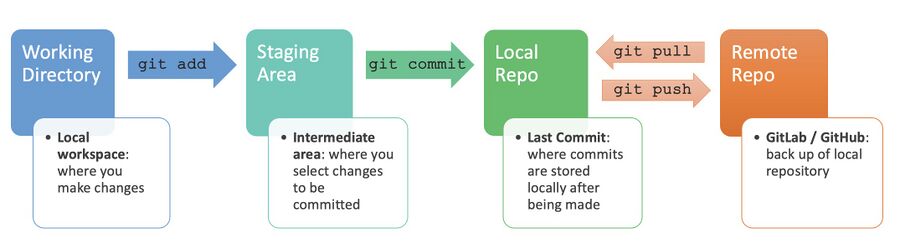
Git Workflow Components
- Working Directory: Your local workspace where you edit files. Changes here are not tracked until moved to the staging area.
- Staging Area: A prep zone for changes to be committed. You can selectively choose which changes to include in a commit.
- HEAD: The latest commit in the current branch, acting as a pointer to your most recent work.
- Local Repository: Your computer's storage for all your commits, branches, and the entire change history. It operates independently of network access.
- Remote Repository: A server-hosted repository (e.g., GitLab, GitHub) for code sharing and backup. It syncs with the local repository through
pushandpullcommands.
Note: For the longest time, the default branch in most Git repositories was named master; the convention is now to name it main. To rename the local master branch:
$ git branch -m master main
To rename the remote master branch, see here.
Git File Status
Tracked vs Untracked Files
- Tracked files are those that Git knows about and has in its version history.
- Untracked files are new or unrecorded files in your working directory that Git isn't keeping track of yet; e.g.
temp/,auto_settings.sav*,auto_positions.sav*, etc.
Staged vs Unstaged
- Staged files are those that have been marked for inclusion in the next commit, showing Git exactly what changes you want to commit.
- Unstaged files are the modified files in your working directory that have not been marked for the next commit yet.
- Why stage? Staging in Git is the process of selecting specific changes you want to include in your next commit. Instead of committing all the changes you've made since the last commit, you can choose a subset of these changes to commit.
Git add
The git add command is used for both staging changes and beginning to track new files:
- Staging Changes: When you modify a file that is already being tracked by Git (i.e., it's been committed at least once before), using
git add <filename>stages these changes. This means you're marking the modifications in that file to be included in the next commit. - Tracking New Files: For new files that are not yet tracked by Git (they have never been committed),
git add <filename>starts tracking these files in addition to staging them. From this point onward, any changes to these files will be recognized by Git.
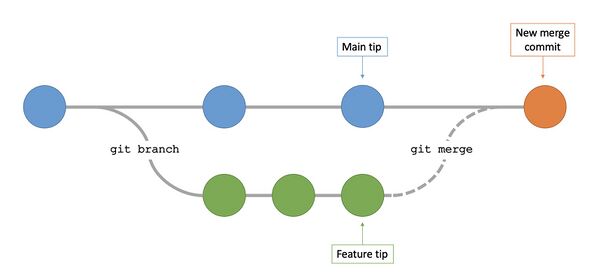
Branching Basics
Branching Overview
- What is a Branch?
It's essentially a separate line of development. You can think of it as an independent line of work that doesn't interfere with others.
- Why Use Branches?
They allow you to work on new features, bug fixes, or experiments in isolation from the main (deployed) code. Branches facilitate parallel development, enabling multiple team members to work on different aspects simultaneously without stepping on each other's toes.
- How Does it Work?:
When you create a branch in Git, you're creating a new pointer to commits. It's like a bookmark on your work, allowing you to switch contexts quickly. Changes made in a branch don't affect other branches. You can merge these changes back into the main branch when they're ready.
Typical Branching Workflow
- Create a new branch from the
mainbranch:
$ git checkout main # Switch to (or confirm you are on) the main branch $ git pull # Ensure it's up to date with the remote $ git checkout -b new-branch # Create a new branch and switch to it
Note that because of the -b option in git checkout -b new-branch, this command is equivalent to git branch new-branch + git checkout new-branch, i.e. create a branch and switch to it.
- Make your changes in this new branch and test them to ensure they work as intended.
- Add and commit your changes:
$ git add <modifiedfile> $ git commit -m "Your commit message"
- Merge the branch back into
mainonce your work is complete:
$ git checkout main # Switch back to the main branch $ git pull # Update the main branch (just in case) $ git merge new-branch # Merge the new branch into main $ git push # Push the updates to the remote repository
This workflow assumes you're starting from and merging back into a branch named main. Replace main with the appropriate branch name if different in your repository.
Troubleshooting
Git Status Explained - General Case
$ git status
On branch main
Your branch is up to date with 'origin/main'.
Changes to be committed:
(use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
modified: file1
new file: file2
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: file3
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
temp/
notes.txt
- On Branch: You're currently on the
mainbranch. - Branch Status: Your
mainbranch is up to date withorigin/main(the main branch from the remote repository). - Changes to be Committed:
file1has been modified andfile2is a new file, both staged for the next commit.- To unstage, use
git reset HEAD <file>.
- Changes Not Staged for Commit:
file3is modified but not staged.- To stage, use
git add <file>. - To discard changes, use
git checkout -- <file>.
- Untracked Files:
temp/andnotes.txtare not tracked by Git.- To track, use
git add <file>. - To ignore, add them to the
.gitignorefile
Your branch is ahead of 'origin/main'
$ git status On branch main Your branch is ahead of 'origin/main' by 3 commits. (use "git push" to publish your local commits) nothing to commit, working tree clean
- On Branch: You're currently on the
mainbranch. - Branch Status:
- Your
mainbranch is ahead oforigin/mainby 3 commits. This means you have made commits locally that are not yet in themainbranch on the remote repository. - To synchronize these changes with the remote repository, use
git push.
- Your
- Working Tree Status:
- Your working directory is clean, meaning there are no unstaged changes or untracked files.
Your branch is behind 'origin/main'
$ git status On branch main Your branch is behind 'origin/main' by 2 commits, and can be fast-forwarded. (use "git pull" to update your local branch) nothing to commit, working tree clean
- On Branch: You're currently on the
mainbranch. - Branch Status:
- Your
mainbranch is behindorigin/mainby 2 commits. This indicates that there are updates on the remote repository that you don't have locally. - You can fast-forward your local branch to catch up with
origin/mainusinggit pull.
- Your
- Working Tree Status:
- Your working directory is clean, meaning there are no unstaged changes or untracked files.
Your branch and 'origin/main' have diverged
$ git status
On branch main
Your branch and 'origin/main' have diverged,
and have 1 and 2 different commits each, respectively.
(use "git pull" to merge the remote branch into yours)
You have unmerged paths.
(fix conflicts and run "git commit")
(use "git merge --abort" to abort the merge)
Unmerged paths:
(use "git add <file>..." to mark resolution)
both modified: conflicted_file.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
- On Branch: You're currently on the
mainbranch. - Branch Divergence:
- Your local
mainbranch and remoteorigin/mainbranch have diverged. This means there are different commits in both branches that are not in the other.
- Your local
- Merge Conflict:
- A merge conflict has occurred in
conflicted_file.txtdue to differing changes from both the local and remote branches. - To resolve the merge conflict, manually edit the file to reconcile the differences, then use
git add <file>to mark the conflict as resolved. - After resolving the conflict, complete the merge by committing the changes with
git commit. - If you wish to cancel the merge, use
git merge --abort.
- A merge conflict has occurred in
- Working Tree Status:
- Address the merge conflict before proceeding with other Git operations.
- For more info on addressing conflict, see here.