Air Sensitive Samples
Information for 11-BM users who have mail-in samples that are moisture or atmosphere sensitive.
Introduction
Many mail-in users for powder diffraction at 11-BM have successfully sent and measured atmosphere sensitive samples. Most users send either 1) samples with powders directly sealed inside the Kapton capillary tubes supplied by the beamline using epoxy on the tubes ends, or 2) samples sealed inside extra [glass or quartz sealed capillaries https://wiki-ext.aps.anl.gov/ug11bm/index.php/Using_Glass_or_Fused_Quartz_Capillaries] which are then nested inside the Kapton tubes before sending to the beamline.
Both methods could be used with sample powders prepared and loaded inside a glove box.
NOTE that ALL samples must fit completely inside the supplied Kapton tubes. Glass capillaries without Kapton protection, or glass capillaries that are longer than the Kapton tubes will NOT be accepted for the mail-in program and will be disposed at the beamline on receipt before any measurements.
For a guide about how to prepare glass capillaries INSIDE of the Kapton tubes, see our wiki page for Nesting_Glass/Quartz_Capillaries_in_Kapton_Tubes
2
Nested glass or quartz capillaries is one option, see more here:
https://wiki-ext.aps.anl.gov/ug11bm/index.php/Nesting_Glass/Quartz_Capillaries_in_Kapton_Tubes
Also, many users have experienced good luck with simply using the Kapton tubes, but with the end sealed by quick dry epoxy. This has worked well for many users with, for example, Li transition metal type air sensitive samples. For extra protection, you could ship the capillaries and mounting bases inside sealed containers that we would open just prior to any scans.
Please note that the APS will close for a winter shutdown period next week. We will try to run as many samples as possible before the shutdown, but if samples arrive later we will hold them until operations resume in February.
http://www.aps.anl.gov/Users/Calendars/GUP_Calendar.htm
best 11BM staff
Shipping Atmosphere-Sensitive Samples
If a sample must be shipped in a special (e.gg., inert or dry) atmosphere, the magnetic bases and plastic caps can be sealed in screw-top glass vials. Care must be taken that the glass containers do not break from motion of the sample mount inside nor from hitting each other. For example, the glass vials should be protected from one another by some sort of separator, such as padding. Likewise, motion of the sample mount inside the vial must be restricted to keep the mount from hammering the glass. Both of these problems have occurred in samples shipped to the beamline and resulted in the samples becoming useless.
Do not simply seal the samples in flame-sealed glass. We do not have the means of opening such samples nor of handling the resulting glass shards.
Practical Example
Dear Marine
Thanks for you email. Great news that your Kapton sealed samples were similarly preserved when compared to the flame sealed glass capillaries. A big advantage with Kapton is that these are much more likely to survive intact when shipped to the beamline for measurements,
If you are able to share some experimental details (how the tubes were sealed, epoxy?) and the sample chemistries, I could mention this example from your group (and any future publications) when speaking with other mail-in users who are equally concerned about shipping atmosphere sensitive samples.
You will find enclosed a small report which compares the patterns obtained with the epoxy-sealed kapton tubes to the ones obtained with the flame-sealed quartz capillaries. It also provides some details about the samples preparation. Please, let me know if you need more information. I still have one 1.5mm kapton tube that we could use for an additional test if you want.
On May 30, 2013, at 1:32 , Marine REYNAUD <[email protected]> wrote:
Dear Matthew,
Thank for your e-mail.
Yes we have recently finished the refinement of the samples measured in the kapton tube and in the
glass capillaries. Epoxy-sealing of the kapton tube is pretty good. We haven't noticed any oxidation of
the samples and the quality of the data is improved if we do not used glass capillaries. I will send
you a small
Reynaud, M.; Ati, M.; Melot, B. C.; Sougrati, M. T.; Rousse, G.; a, J.-N. C.; Tarascon, J.-M. "Li2Fe(SO4)2 as a 3.83 V positive electrode material Electrochemistry Communications 2012, 21, 77–80.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1388248112001932
Comparison of the atmosphere protection
of epoxy-sealed Kapton tubes vs. flame-sealed quartz capillaries for Synchrotron X-ray diffraction measurements Marine Reynaud, Joshua A. Kurzman
Laboratoire de Réactivité et Chimie des Solides, Université de Picardie Jules Verne, 33 rue Saint Leu, 80039 Amiens cedex, France. E-mail: [email protected] (permanent one: [email protected]), [email protected] (permanent one : [email protected])
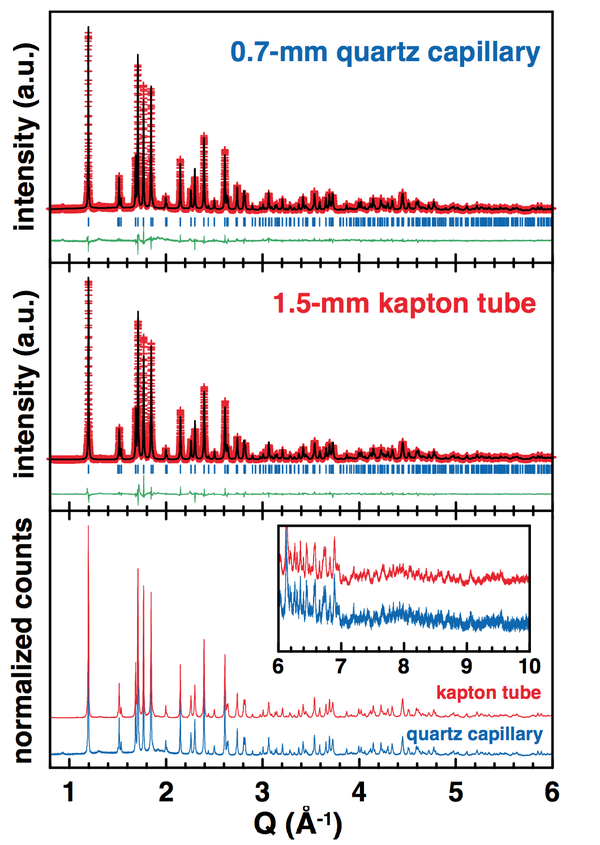
Collection of X-ray diffraction patterns for air- and/or moisture-sensitive samples can be an issue. Two options are currently proposed for the preparation of such samples for their measurement via the 11-BM mail-in service. The first one is to seal the sample into a Kapton tube using epoxy glue; however the gas permeability of Kapton was not really known up to now. Alternatively, the sensitive powders can be sealed in a glass or quartz capillary, prior being nested in the Kapton tube; however these capillaries are more likely to be broken during the shipment to the beamline, and the quality of the data may be reduced by the use of the extra glass or quartz capillary. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to evaluate the effectiveness of the atmosphere protection of epoxy-sealed Kapton tubes compared to flame-sealed quartz capillaries. Two samples of different degree of air/moisture-sensitivity were measured in both conditions (epoxy-sealed kapton tube and flame-sealed quartz capillaries) through the 11-BM mail-in service.
Samples preparation
Epoxy-sealed Kapton tubes: 1.5-mm diameter Kapton tubes were first fixed to the sample base using one drop of epoxy glue in the open air. Then the powder samples were filled into the kapton tubes inside an argon-filled glove- box, and the tubes were sealed with another drop of epoxy glue. Note that the epoxy glue takes more time to dry under argon than under air, and at least one night was needed for the glue to harden in the glove-box. For the shipment, the bases were then packed into a coffee-bag sealed under argon, which was opened by the 11-BM staff only few hours before the XRD measurement.
Flame-sealed quartz capillaries: 0.7-mm diameter quartz capillaries were filled with the powder samples into an argon-filled glove- box. After being plugged with a drop of epoxy-glue under argon, the capillaries were brought out of the glove-box and immediately sealed with the flame of a lighter. Then, the as-sealed capillaries were fitted into 0.8-mm diameter kapton tubes and securely fixed with clay or glue. Note that in this case, the sample bases were packed under air to be sent to the 11-BM beamline.
Results
Sample 1: LiFe(SO4)2
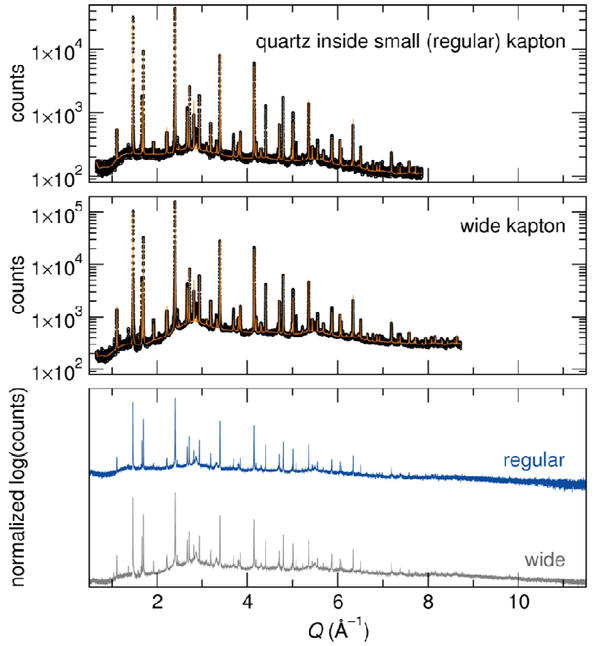
LiFe(SO4)2 is not highly air-sensitive, but it does catch water if exposed few hours to air. The hydrated sample would then present a completely different XRD pattern from the anhydrous phase. As seen from the refinement of the XRD patterns (figure below), both quartz capillary and Kapton tube have efficiently protected the LiFe(SO4)2 sample from moisture. However, one should note that the statistics is definitely improved when using the wider kapton tube (1.5-mm vs. 0.8 mm).
Sample 2: Na3SO3N
Na3SO3N is much more sensitive than LiFe(SO4)2, as it decomposes within a few minutes when exposed to air. However, despite the highly air-sensitive nature of this material, there is no evidence of decomposition in the diffraction pattern collected for the Na3SO3N sample sealed in the wide Kapton tube. As seen from a comparison of the top and middle panels in the figure presented below, the counting statistics are certainly improved by use of the wider tube; which enabled a slightly larger Q range to be refined. Note that, although the different contributions were not separated here, these are 3-phase refinements, and there is evidence for other minor impurities. The primary phase is highly disordered, and the thermal parameters are exceptionally large on all of the atom positions, particularly for those not on special positions, although they agree well with the values reported for comparable Li3PO4 refinements. Therefore, advantages of the wider capillary are perhaps obviated by the intrinsic disorder of the compound.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both epoxy-sealed Kapton tubes and flame-sealed quartz capillaries similarly preserved the samples from air exposure. A noticeable advantage of using epoxy-sealed Kapton tubes is that the entire sample preparation can be carried out in the glove-box, whereas sealing the quartz capillaries with a flame presents the risk of oxidizing the sample. Moreover, Kapton tubes are much less likely to be broken during the shipment or the manipulation of the sample compared to quartz capillaries. Lastly, using a larger diameter Kapton sample tube noticeably improves the counting statistic of the XRD pattern.