Difference between revisions of "34ID-E Coordinate Systems"
From 34-ID-E
Jump to navigationJump to search (→X-Y-Z) |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
=== X-Y-Z === | === X-Y-Z === | ||
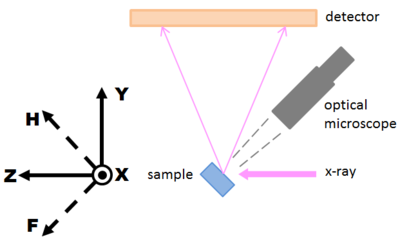
[[Image:Coordinates_beamline.png|right| | [[Image:Coordinates_beamline.png|right|thumb|400px|34IDE beamline XYZ and XHF coordinate systems, side view from outside of the ring.]] | ||
* X: radial direction of the ring, horizontal, pointing outboard to the doors. | * X: radial direction of the ring, horizontal, pointing outboard to the doors. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
=== X-H-F === | === X-H-F === | ||
Because we routinely deal with motions in 45°-tilted directions, H and F are introduced as alternative coordinates to Y and Z: | Because we routinely deal with motions in 45°-tilted directions, H and F are introduced as alternative coordinates to Y and Z: | ||
* H: | * H: 45° upward-downstream (combination of +Y and +Z), this is the typical movement direction of the [[Differential Aperture|depth-profiling wire]]. | ||
* F: | * F: 45° downward-downstream (combination of -Y and +Z), this is the "focus" direction of the sample under the optical microscope. | ||
<math>H = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}(Y+Z)</math> | |||
<math>F = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}(-Y+Z) </math> | |||
<br clear=all> | |||
== Detector Coordinates == | == Detector Coordinates == | ||
== Coordinate Systems in Data Analysis == | == Coordinate Systems in Data Analysis == | ||
Revision as of 21:40, 4 October 2013
| (This article/section is incomplete, please check back again or help expanding it) |
Beamline Coordinates
X-Y-Z
- X: radial direction of the ring, horizontal, pointing outboard to the doors.
- Y: vertically upward (against gravity).
- Z: along the x-ray beam
X-H-F
Because we routinely deal with motions in 45°-tilted directions, H and F are introduced as alternative coordinates to Y and Z:
- H: 45° upward-downstream (combination of +Y and +Z), this is the typical movement direction of the depth-profiling wire.
- F: 45° downward-downstream (combination of -Y and +Z), this is the "focus" direction of the sample under the optical microscope.
<math>H = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}(Y+Z)</math>
<math>F = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}(-Y+Z) </math>